Predictive and condition-based maintenance (PdM / CbM) are both maintenance types that occur before breakdowns happen. As such, they are both forms of proactive maintenance and are designed to increase reliability and decrease downtime.
The primary difference between them is the way in which maintenance is measured. Predictive maintenance relies on precise formulas in addition to sensor measurements (temperature, vibration, noise), and maintenance work is performed based on the analysis of these parameters. In this way, predictive maintenance is a very exact form of maintenance because it predicts future maintenance events.
On the other hand, condition-based maintenance relies only on real-time sensor measurements. Once a parameter reaches an unacceptable level, maintenance workers are dispatched. This means that condition-based maintenance systems perform work only in the moment it is needed.
Both predictive and condition-based maintenance can be expensive to initiate, though they both justify their upfront cost by saving money on downtime and equipment maintenance. Condition-based maintenance in particular can be expensive due to the cost of maintaining sensor devices, so it’s best used on critically important equipment.
Differences between predictive maintenance and condition-based maintenance
| Preventive Maintenance | Condition-based Maintenance | |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Predictive maintenance (PdM) is work that is scheduled in the future based on analysis of sensor measurements and formulas. | Condition-based maintenance (CbM) is work that is performed at the exact moment when measured parameters reach unacceptable levels. |
| Workflow | 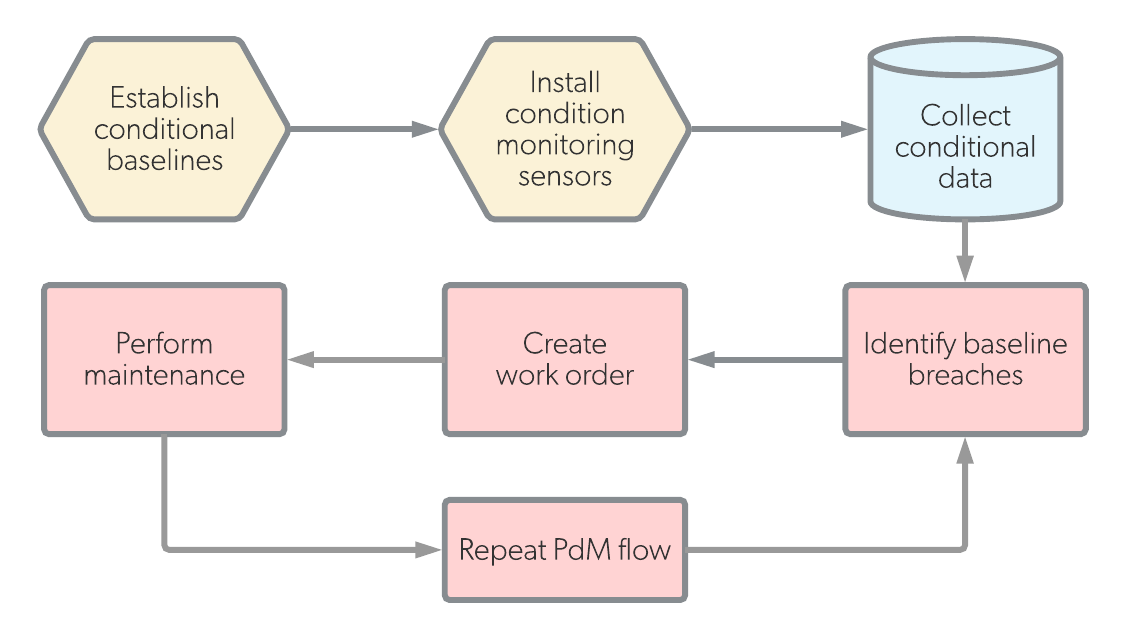 |
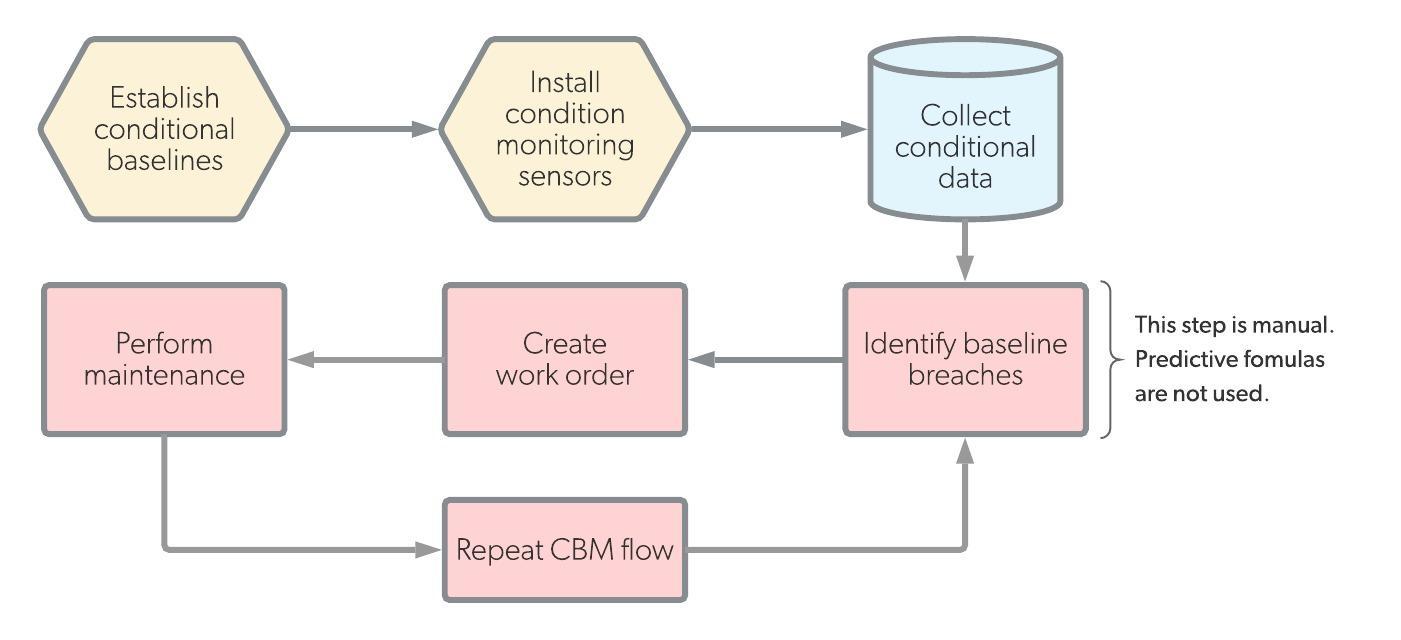 |
| Trigger | Predicted date | Measured parameter level |
| Cost | Medium/High | Medium/High (startup cost) |
| Cost Savings | 25% to 30% | Dependent on amount of equipment using CbM |
| Resources Needed |
|
|
| Pros |
|
|
| Cons |
|
|
| Use Case | An organization has assets with slow-speed bearings that frequently fail. Preventive maintenance is already in place but the organization suspects that assets are being over-greased. To perform maintenance with more precision, they use ultrasound analysis (good for slow-speed bearings). Now, work orders for greasing are only scheduled when certain ultrasound measurements are reached. | An organization needs to make sure that a critical piece of safety equipment can be maintained while it is running at load. One critical equipment parameter is the amount of vibration produced. The organization decides to implement CbM so that maintenance is performed only when vibrations begin to reach unsafe levels. This way, the safety equipment can be run constantly during maintenance and only receives maintenance when necessary. |

![[Review Badge] Gartner Peer Insights (Dark)](https://www.datocms-assets.com/38028/1673900494-gartner-logo-dark.png?auto=compress&fm=webp&w=336)
