What is level of repair analysis (LORA)?
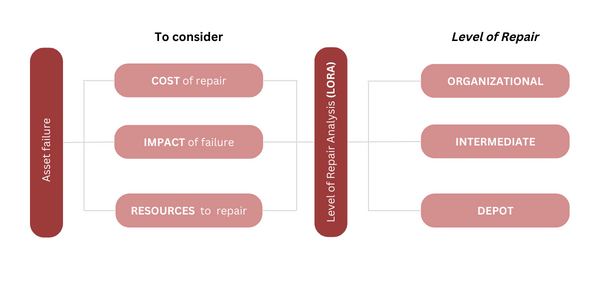
Level of repair analysis (LORA) is a process used to determine when and where an asset should be repaired. LORA is intended to optimize repair decisions in order to minimize the overall life cycle costs of assets. The LORA process takes into account numerous factors, including:
- The costs of different types of repairs, including diagnostics, parts, and labor
- The impact asset failure could have on operations
- The skills and equipment needed to complete specific repairs
After assessing what it would take to repair specific issues and how necessary those repairs would be, LORA determines the type of repair work that should be done and who should do it.
Under this methodology, you’ll typically have three repair levels to choose from. These levels are essentially where repair work is performed:
- Organizational level (O-level), which is performed on the asset on site
- Intermediate level (I-level), which is performed in dedicated maintenance areas or backshops
- Depot level (D-level), which is performed off site, such as at an OEM factory
How to do a level of repair analysis
For example, if a component were to break on a conveyor system, LORA would determine which of the following would be most appropriate:
- Send a team of technicians to perform repairs at the conveyor’s location (O-level)
- Take the broken part to a central shop (I-level)
- Send the asset to the manufacturer for repairs (D-level)
In some cases, certain repairs would be considered too expensive, in which case preventive maintenance performed by a lower repair level would be preferred.
On the other hand, some failures wouldn’t be frequent enough to warrant continuous preventive measures. If they’re severe enough or happen to an asset that’s central to your operations, however, you’d still need to take care of it, even though it would require a higher (and likely more costly) repair level.
Key Takeaways
The ultimate goal of level of repair analysis is to make sure each asset gets exactly the amount of attention it needs to keep cycle life costs to a reasonable level while still meeting your operational requirements.
Want to keep reading?
When should I perform preventive maintenance on equipment?
The Advantages & Disadvantages of Preventive Maintenance
When should I repair or replace an asset?
4,000+ COMPANIES RELY ON ASSET OPERATIONS MANAGEMENT
Leading the Way to a Better Future for Maintenance and Reliability
Your asset and equipment data doesn't belong in a silo. UpKeep makes it simple to see where everything stands, all in one place. That means less guesswork and more time to focus on what matters.

![[Review Badge] Gartner Peer Insights (Dark)](https://www.datocms-assets.com/38028/1673900494-gartner-logo-dark.png?auto=compress&fm=webp&w=336)