What is infrared analysis?
Infrared analysis uses infrared radiation to compare the difference in temperature between components in one view or multiple views over time. The temperature differences can indicate an asset’s condition or performance.
radiation (IR) is the wavelength of light that is invisible to the human eye. The varying levels of light indicate an object’s temperature.
Overview
The use of IR measurement equipment offers substantial financial savings to organizations that use it. The Federal Energy Management Program (FEMP) says a savings of 30% to 40% is possible for equipment that is only served by a reactive maintenance program.
IR is valuable in determining:
- Temperature variations of mechanical components such as bearings or motor cases
- The condition of electrical components (prevalent for ARC flash analysis)
- Process temperatures
- Insulation or building conditions
- Piping and plumbing conditions
- Solar panel conditions (a new use for many building owners)
As infrared analysis measures the wavelength of light, it’s important to understand what light waves are and what they are not.
Light waves can become visible when someone gets a sunburn from being outside. It is the invisible energy that radiates from the sun that causes sunburn. Microwave ovens use IR to warm your food.
Do not think that IR comes only from something that you may consider hot. Light waves come from all objects regardless of their temperature. The difference is the energy level or wavelength detected upon a spectrum of waves. The reflection from the IR unit is called a signature.
Types of IR applications
Firefighters began using IR to look for occupants of a building on fire. Military and law enforcement use IR to find subjects and hunters use IR to find prey.
Less dramatic usage of IR is its use in measuring temperature differences of building construction or process piping. Determining the performance of insulation or piping conditions offers substantial rewards for those using IR. Building owners can obtain an image of their buildings’ needs.
IR can be used for a singular event or as a part of a predictive maintenance (PdM) program. Unique events can include one-time views of an object to determine its conditions.
Mechanical analysis
Equipment operating at any speed generates heat. Images reflect the varying energy levels of each component in a scan. Elements that are the brightest have the highest temperature. Overheated parts cause failures.
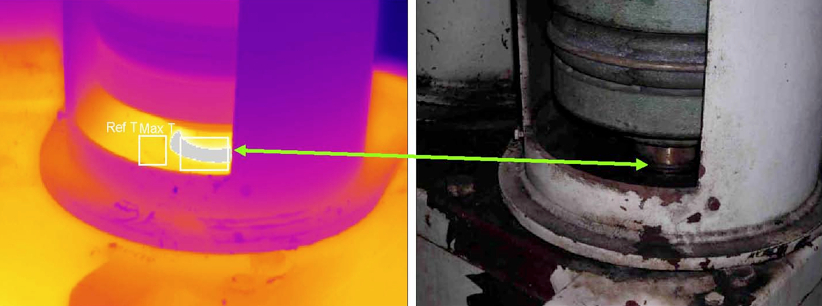
An IR scan showing a failed bearing. Image courtesy of Reliability Web.
In the example illustrated above, an IR scan shows a bearing at risk of failing shortly after it was installed. One-time or inspection activities can be conducted using the power of IR. This test was used to determine the quality of the motor that was installed. Conducting the test prevented an unexpected failure and provided feedback to the motor supplier. The root cause was determined to be the way the motor had been stored in the customer’s parts room.
Electrical failures
Poor electrical connections generate heat and heat causes damage. Infrared analysis is powerful in locating potential electrical failures due to its ability to isolate temperature differences. A poor connection is quickly identified using IR.
An electrical connection that is mechanically loose will increase resistance. Increased resistance causes amperage to increase and increased amperage creates heat that can cause several failures.
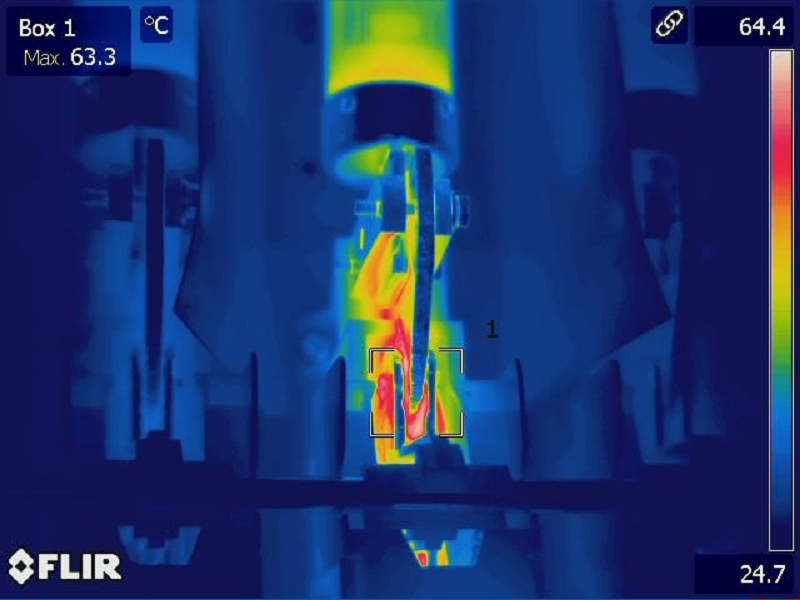
An IR scan showing an electrical failure caused by a loose connection. Image courtesy of Infrared Imaging Services.
Arc flash
Estimates are that 10 to 15 serious arc flash incidents occur every day in the US. These events may require severe burns sending personnel to burn centers for treatment. IR has proven to be a safe and useful tool for identifying potential ARC flash risk locations.
ARC flash can occur when conditions change inside an electrical container. IR does not prevent or predict ARC Flash from happening. Instead, its use can indicate hot spots where further inspection may be needed.
Safety Note: ARC flash is a hazardous condition that can occur when exposing electrical enclosures. Be sure that you adhere to all of your organization’s safety requirements when opening electrical enclosures.
Insulation and building conditions
Building contractors and owners quickly adopted IR to determine the quality of their efforts to separate outside conditions form the inside. They were even able to assess damage and the location of mold with IR.
Measurements taken for insulation and building condition analysis use passive IR. Passive IR measures material that is not generating a temperature difference.
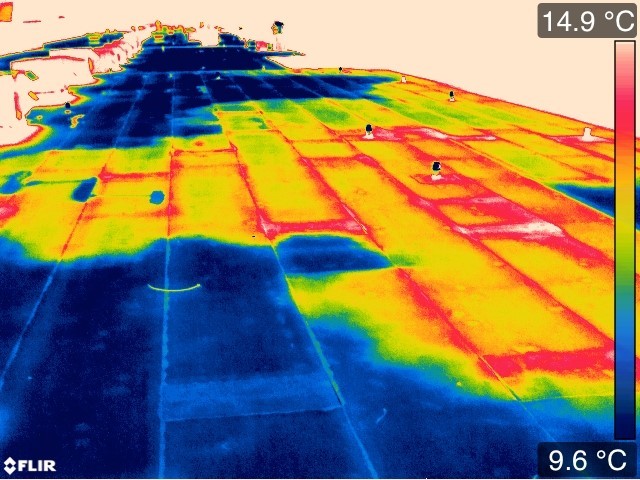
An IR scan showing a roof with areas of poor insulation. Image courtesy of Infrared Imaging Services.
This picture shows a “hot” spot where thermal energy is passing through a building’s roof. The potential cause is inadequate or missing insulation. The building’s occupants are losing money to make up for the heat lost at this location.
Pipe and leak detection
IR’s ability to quickly detect temperature differences makes it a useful tool for locating potential areas of energy or fluid loss in pipes.
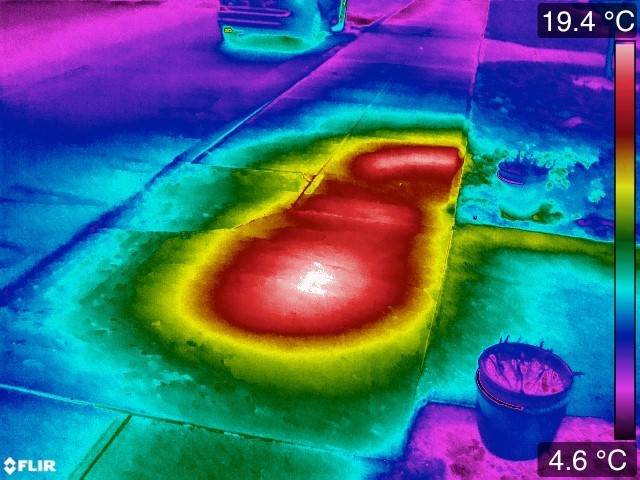
An IR scan showing a leaking steam pipe beneath a city sidewalk. Image courtesy of Infrared Imaging Services.
Solar panels
Solar panel owners can experience failure with their energy systems, including loss of a single defective cell. The loss of a single cell reduces the equipment’s generating power and can even cause the entire panel to fail. With IR technology, you can identify these defective cells and apply a precise fix.
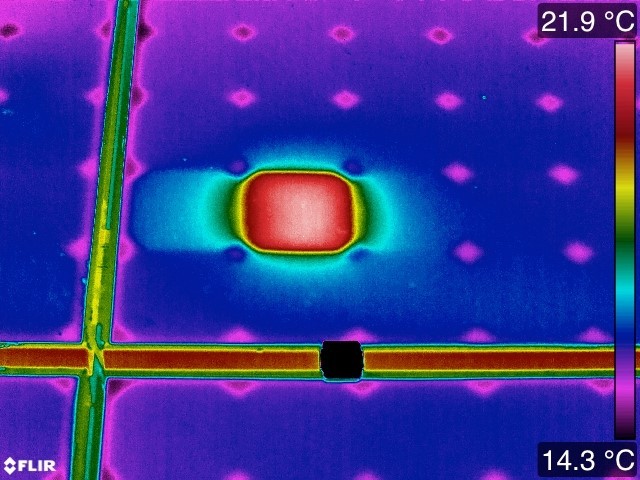
An IR scan showing a suspect solar panel cell. Image courtesy of Infrared Imaging Services.
Conclusion
Infrared analysis is a cost-effective way to identify imminent or existing problems with various types of assets, components, and materials. And unlike oil analysis and other types of predictive maintenance that require intense training, IR is relatively easy to adopt. For these reasons, organizations around the world are using IR to move from preventive maintenance to predictive maintenance and find existing failures faster.

![[Review Badge] Gartner Peer Insights (Dark)](https://www.datocms-assets.com/38028/1673900494-gartner-logo-dark.png?auto=compress&fm=webp&w=336)
