What metrics are most important for inventory management?
Techniques to manage inventory can vary depending on the type of inventory being kept and the nature of the business. For example, a retail organization keeping stock to sell would manage inventory differently than a maintenance, repair, and operations (MRO) department stocking up on spares.
Some of the most important metrics to prioritize in terms of maintenance inventory management are the following:
1. Inventory turns
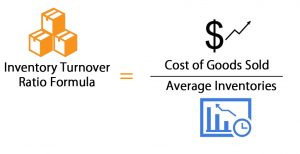
Inventory turns, also known as inventory turnover, is a measure of how quickly stock is being used. It is measured by taking the value of stock purchased over a period of time, divided by the current value of the stock on hand. This gives an estimate of how much stock is being replenished, therefore giving insights on how fast inventory is flowing through.
Best practice values can range from 1.0 when considering the total inventory, to 3.0 when considering inventory without critical spares.
2. Inventory accuracy
It is important to accurately monitor that the current value of stock in the warehouse. If actual, physical stock is not accurately represented in analysis reports, planning efforts are put to waste.
The most obvious way to check inventory accuracy is through tediously performing inventory counts. Though effective, this method is extremely inefficient. To ensure inventory accuracy while significantly reducing the effort required, an efficient tagging procedure such as a barcode system can be used to track the physical movement of stock.
3. Stock-out occurrences
Having spares in stock makes way for seamless maintenance procedures. Depending on a spare’s criticality, a stock-out occurrence can cause you serious downtime. Remember that not all spares can be bought off the shelf. Therefore, some spares have the potential to hold up operations for long periods of time.
Tracking the occurrences of stock-outs can give the team insights on the amount of time they can save by improving inventory management. Best practices for inventory stock-outs is less than 2% of total inventory requests.
4. Inventory value
It makes sense to keep track of stock not only based on quantities but also on monetary value. By maximizing the features of your computerized maintenance management system (CMMS), the value of inventory on hand can be more easily tracked and calculated.
Inventory value can be compared to the estimated plant replacement value (PRV) to put the costs in context and have a feel for whether you are holding too much or too little. SMRP best practices suggest the inventory value to be less than 1.5% of the PRV.
5. Obsolete inventory
As an extension of keeping track of your inventory value, it is important to also know how much of it is becoming obsolete. Obsolete inventory includes products that a company had purchased that can no longer be used or sold. Spares that are obsolete incur costs without providing useful value.
Want to keep reading?
How to Measure Inventory Performance with Inventory Management Metrics
What is the true cost of poorly optimized inventory management?
7 Metrics You Should Be Tracking for Maintenance Inventory
4,000+ COMPANIES RELY ON ASSET OPERATIONS MANAGEMENT
Leading the Way to a Better Future for Maintenance and Reliability
Your asset and equipment data doesn't belong in a silo. UpKeep makes it simple to see where everything stands, all in one place. That means less guesswork and more time to focus on what matters.

![[Review Badge] Gartner Peer Insights (Dark)](https://www.datocms-assets.com/38028/1673900494-gartner-logo-dark.png?auto=compress&fm=webp&w=336)
