Preventive maintenance and breakdown maintenance both seek to maintain and repair equipment, but they have very different ways of doing this.
What’s the main difference between preventive and breakdown maintenance?
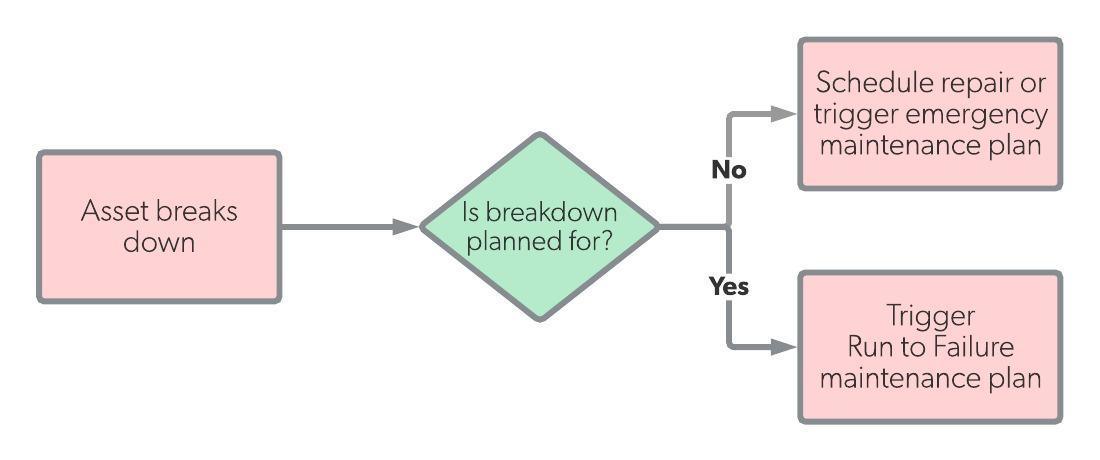
Preventive maintenance identifies any issues before equipment failure or downtime, through routinely scheduled maintenance. Breakdown maintenance works by running equipment until it breaks down, in which case repairs and maintenance are performed.
Preventive maintenance operates based on a schedule, where maintenance tasks are completed at specific intervals prior to downtime events. This is because the goal of preventive maintenance is to maximize the lifespan and runtime of equipment.
Breakdown maintenance is somewhat specific because it’s not applicable to many pieces of equipment. For example, it is not a suitable maintenance strategy for anything involved in human safety and health, nor is it a good strategy for critical or central pieces of equipment.
However, it works well with things that are designed to be used until they’re inoperable. This can include everything from light bulbs to residential water heaters.
Even though a water heater may be considered a critical piece of equipment, the time spent PMing a water heater—which includes disrupting the resident every X months—is probably more intrusive than fixing a broken system every decade or so. This shows that breakdown maintenance is applicable for critical pieces of equipment in certain cases, especially in the property management space.
Preventive maintenance, on the other hand, is a solid maintenance plan for almost all pieces of equipment in a factory setting. In a residential setting, however, it only makes sense to perform PMs on equipment in non-living areas.
Differences between preventive and breakdown maintenance
| Preventive maintenance | Breakdown maintenance | |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Preventive maintenance (PM) is work that is scheduled based on calendar time, asset runtime, or some other period of time. | Breakdown maintenance (BM) is work that is only performed when a piece of equipment breaks down or has a downtime event. |
| Workflow | 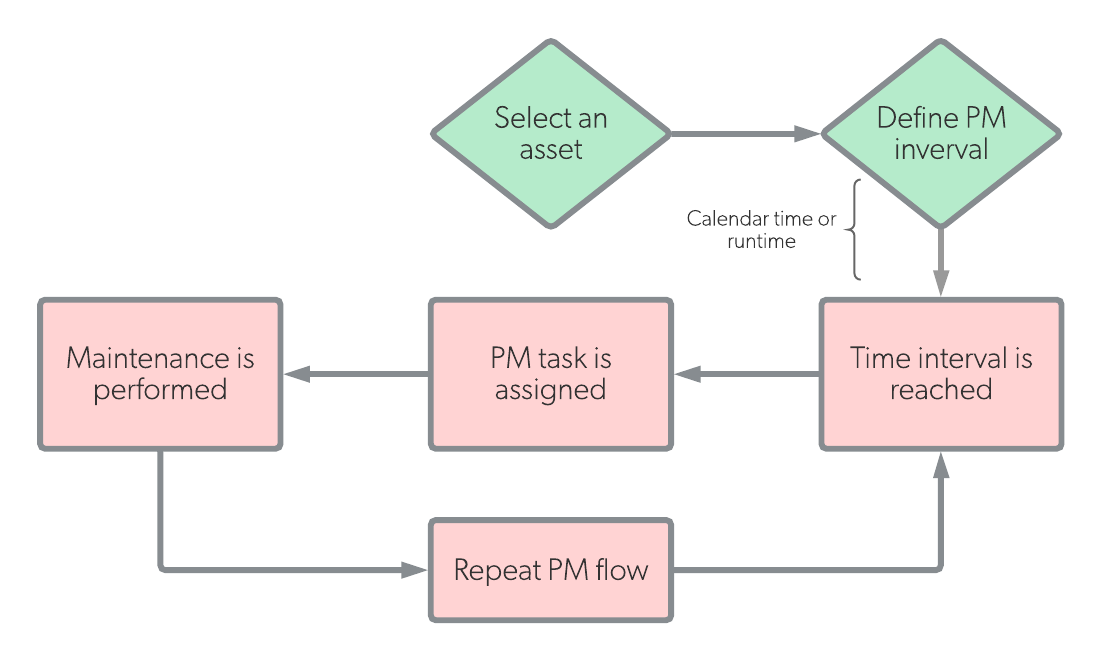 |
 |
| Trigger | Time | Downtime event |
| Cost | Low | Low |
| Cost Savings | 12% to 18% [1] | Dependent on equipment and breakdown maintenance plan |
| Resources Needed |
|
|
| Pros |
|
|
| Cons |
|
|
| Use Case | An organization wants to decrease unplanned downtime and emergency maintenance but does not have a large maintenance budget. As a solution, they implement a PM program for select assets. Work orders are scheduled for inspections, lubrication, filter replacements, and parts replacements based on recommendations from OEMs. | An organization wants to lower the cost of constantly replacing a variety of light bulbs in a facility. Instead of replacing them at designated intervals, the organization decides to adopt a breakdown maintenance plan, only replacing light bulbs when they are completely burned out. This saves time and reduces the overall cost of buying light bulbs as the necessary amount of spares is lower. |
[1] Types of Maintenance Programs by the Department of Energy, O&M Best Practices Guide, Release 3.0

![[Review Badge] Gartner Peer Insights (Dark)](https://www.datocms-assets.com/38028/1673900494-gartner-logo-dark.png?auto=compress&fm=webp&w=336)
